Cube GUI
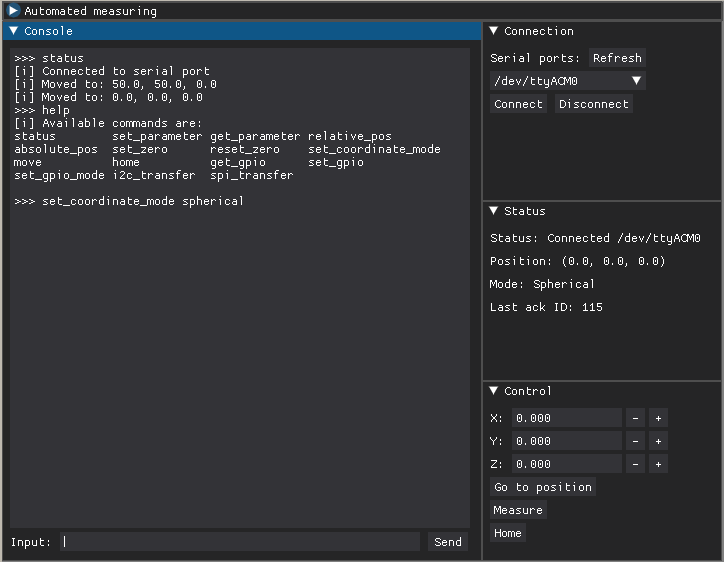
Cube GUI is a simple, DearPyGUI, multiplatform application for controlling the cube.
Current features include: - Setting up serial ports for communication - Exposing a cmd-like interface for manual control - Controling movement - Ability to add custom sensor communication functions - Automated grid measurement with export to .CSV file
GUI Sections
Each section can be collapsed and move around as a separate sub-window in top level GUI window.
The Automated measuring section is collapsed by default.
Connection
Facilitates the connection via serial link to the hardware.
Serial ports: Lists all current serial ports detected
Refresh: Refreshes the list of the ports
Connect: Opens connection via the selected serial port
Disconnect: Terminates the connection
Status
Provides various status info, such as general status, current position, current coordinate mode etc.
Control
Has interface for movement control.
X, Y, Z: Set the desired XYZ position
Go to position: Go to the set position
Measure: if the measure function is provided, runs it
Home: Start the homing procedure
Console
Provides a console-like control interface for the Cube. Result of all the operations are written here. You can type your own commands manually in the bottom text field.
Available commands
Type help to list available commands.
Detailed list of commands:
help: list the available commandsstatus: send status instructionrelative_pos: get the current relative positionabsolute_pos: get the current absolute positionset_zero: set the current position as relative zeroreset_zero: reset the relative zero to absolute zerohome: start the homing procedureget_parameter ID: get the parametrID's value.IDis decimaluint32_t.set_parameter ID VALUE: set the paramterIDtoVALUE. BothIDandVALUEare decimaluint32_t.set_coordinate_mode {cartesian|cylindrical|spherical}: sets the coordinate modemove X Y Z: move to a position.X Y Zare decimal floats.get_gpio INDEX{0-15}: get value of GPIO of selected indexset_gpio INDEX{0-15} BOOL: set value of GPIO of selected indexset_gpio_mode INDEX{0-15} BOOL: set the GPIO to input or outputi2c_transfer RX_LEN{0-64} TX_LEN{0-64} ADDR DATA: make a I2C transfer to device with addressADDR. SendsRX_LENbytes ofDATA, then receivesTX_LENbytes.DATAhas to be a string of hexadecimal values with no spaces (ie,0x74 0xAF 0x01should be74AF01).ADDRis also a hex value with no prefix (ie,58or7C).spi_transfer CS{0-3} MODE{0-3} LEN{0-64} DATA: make an SPI transfer of lengthLENon the bus. Use chip select with indexCS. The bus will useMODEfor the CPOL/CPHA setting number (refer to wikipedia).DATAhas to be a string of hexadecimal values with no spaces (ie,0x74 0xAF 0x01should be74AF01).
Automated measuring
Can be used to do an automated grid measurement and save results to an output file. The scanned volume is a grid in the current coordinate system, so for cylindrical and spherical modes, it is not a cube, but a cylinder and sphere, respectively.
It is required to provide the measure and init functions to use this functionality. The software will step through all the grid positions, run the measurement function and save the output data to a .csv file.
Start position: The start position of the grid
Step size: Spacing between measurement points
Number of steps: How many steps per axis
Set current position: Sets the current position as the start position
Select save location: Opens dialog to change the output file location and name
Start measuring: Starts the measurement process
Stop measuring: Should stop the measurement process, but currently does not work
Progress: Shows current progress
Supplying custom sensor functions to the GUI
You can provide your own measure and init functions when launching the GUI.
These functions enable you to implement custom interaction with the sensor.
Their interface is simple:
- input argument is a
CubeCommobject from thePyCubeLib - you use this object to interact with the cube - talk to a sensor, do some submovement
- return argument of
measureis a tuple(has_error, error, (x, y ,z)), where:has_erroris a bool indicating errorerroris the error string(x, y, z)is the output tuple with XYZ measurement data (you can use only a single element, but the API always requires three)
- return argument of
initis a boolean value, indicating either successful or failed initialization
Look into the provided example.py for a basic usage example.
CSV export format
A simple .csv file with each line representing a six-dimensional vector: first three elements are the XYZ position in the coordinate system they were measured in, the rest are XYZ data of the measurement.
x_pos, y_pos, z_pos, x_val, y_val, z_val # header
px1, py1, pz1, x1, y1, z1 # measurement data
px2, py2, pz2, x2, y2, z2
px3, py3, pz3, x3, y3, z3
...
...
...